Galaxy morphological classification

Galaxy morphological classification is a system used by astronomers to divide galaxies into groups based on their visual appearance. There are several schemes in use by which galaxies can be classified according to their morphologies, the most famous being the Hubble sequence, devised by Edwin Hubble and later expanded by Gérard de Vaucouleurs and Allan Sandage.
Contents |
Hubble sequence
The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1936.[1] It is often known colloquially as the “Hubble tuning-fork” because of the shape in which it is traditionally represented. Hubble’s scheme divides galaxies into 3 broad classes based on their visual appearance (originally on photographic plates):

- Elliptical galaxies have smooth, featureless light distributions and appear as ellipses in images. They are denoted by the letter E, followed by an integer
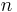 representing their degree of ellipticity on the sky.
representing their degree of ellipticity on the sky. - Spiral galaxies consist of a flattened disk, with stars forming a (usually two-armed) spiral structure, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge, which is similar in appearance to an elliptical galaxy. They are given the symbol S. Roughly half of all spirals are also observed to have a bar-like structure, extending from the central bulge. These barred spirals are given the symbol SB.
- Lenticular galaxies (designated S0) also consist of a bright central bulge surrounded by an extended, disk-like structure but, unlike spiral galaxies, the disks of lenticular galaxies have no visible spiral structure and are not actively forming stars in any significant quantity.
These broad classes can be extended to enable finer distinctions of appearance and to encompass other types of galaxy, such as irregular galaxies, which have no obvious regular structure (either disk-like or ellipsoidal).
The Hubble sequence is often represented in the form of a two-pronged fork, with the ellipticals on the left (with the degree of ellipticity increasing from left to right) and the barred and unbarred spirals forming the two parallel prongs of the fork. Lenticular galaxies are placed between the ellipticals and the spirals, at the point where the two prongs meet the “handle”.
To this day, the Hubble sequence is the most commonly used system for classifying galaxies, both in professional astronomical research and in amateur astronomy.
de Vaucouleurs system




The de Vaucouleurs system for classifying galaxies is a widely used extension to the Hubble sequence, first described by Gérard de Vaucouleurs in 1959.[2] de Vaucouleurs argued that Hubble's two-dimensional classification of spiral galaxies - based on the tightness of the spiral arms and the presence or absence of a bar - did not adequately describe the full range of observed galaxy morphologies. In particular, he argued that rings and lenses were important structural components of spiral galaxies.[3]
The de Vaucouleurs system retains Hubble’s basic division of galaxies into ellipticals, lenticulars, spirals and irregulars. To complement Hubble’s scheme, de Vaucouleurs introduced a more elaborate classification system for spiral galaxies, based on three morphological characteristics:
- Bars. Galaxies are divided on the basis of the presence or absence of a nuclear bar. de Vaucouleurs introduced the notation SA to denote spiral galaxies without bars, complementing Hubble’s use of SB for barred spirals. He also allowed for an intermediate class, denoted SAB, containing weakly barred spirals. Lenticular galaxies are also classified as unbarred (SA0) or barred (SB0), with the notation S0 reserved for those galaxies for which it is impossible to tell if a bar is present or not (usually because they are edge-on to the line-of-sight).
- Rings. Galaxies are divided into those possessing ring-like structures (denoted ‘(r)’) and those without rings (denoted ‘(s)’). So-called ‘transition’ galaxies are given the symbol (rs).
- Spiral arms. As in Hubble’s original scheme, spiral galaxies are assigned to a class based primarily on the tightness of their spiral arms. The de Vaucouleurs scheme extends the arms of Hubble’s tuning fork to include several additional spiral classes:
- Sd (SBd) - diffuse, broken arms made up of individual stellar clusters and nebulae; very faint central bulge
- Sm (SBm) - irregular in appearance; no bulge component
- Im - highly irregular galaxy
Most galaxies in these three classes were classified as Irr I in Hubble’s original scheme. In addition, the Sd class contains some galaxies from Hubble’s Sc class. Galaxies in the classes Sm and Im are termed the “Magellanic” spirals and irregulars, respectively, after the Magellanic Clouds. The Large Magellanic Cloud is of type SBm, while the Small Magellanic Cloud is an irregular (Im).
The different elements of the classification scheme are combined - in the order in which they are listed - to give the complete classification of a galaxy. For example, a weakly-barred spiral galaxy with loosely-wound arms and a ring is denoted SAB(r)c.
Visually, the de Vaucouleurs system can be represented as a three-dimensional version of Hubble’s tuning fork, with stage (spiralness) on the x-axis, family (barredness) on the y-axis, and variety (ringedness) on the z-axis.[4]
Numerical Hubble stage
de Vaucouleurs also assigned numerical values to each class of galaxy in his scheme. Values of the numerical Hubble stage T run from -6 to +10, with negative numbers corresponding to early-type galaxies (ellipticals and lenticulars) and positive numbers to late types (spirals and irregulars). Elliptical galaxies are divided into three 'stages': compact ellipticals (cE), normal ellipticals (E) and transition types (E+). Lenticulars are similarly subdivided into early (S-), intermediate (S0) and late (S+) types.
Hubble stage  |
-6 | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| de Vaucouleurs class[4] | cE | E | E+ | S0- | S00 | S0+ | S0/a | Sa | Sab | Sb | Sbc | Sc | Scd | Sd | Sdm | Sm | Im |
| approximate Hubble class[5] | E | S0 | S0/a | Sa | Sa-b | Sb | Sb-c | Sc | Sc-Irr | Irr I | |||||||
The use of numerical stages allows for more quantitative studies of galaxy morphology.
The Yerkes (or Morgan) scheme
Created by American astronomer William Wilson Morgan. Together with Philip Keenan, Morgan developed the MK system for the classification of stars through their spectra. The Yerkes scheme uses the spectra of stars in the galaxy; the shape, real and apparent; and the degree of the central concentration to classify galaxies.
| Spectral Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| a | Prominent A stars |
| af | Prominent A-F stars |
| f | Prominent F stars |
| fg | Prominent F-G stars |
| g | Prominent G stars |
| gk | Prominent G-K stars |
| k | Prominent K stars |
| Galactic Shape | Explanation |
|---|---|
| B | Barred spiral |
| D | Rotational symmetry without pronounced spiral or elliptical structure |
| E | Elliptical |
| Ep | Elliptical with dust absorption |
| I | Irregular |
| L | Low surface brightness |
| N | small bright nucleus |
| S | Spiral |
| Inclination | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Galaxy is "Face-on" |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | Galaxy is "Edge-on" |
So, for example, the Andromeda Galaxy is classified as kS5.
See also
- Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies
- Galaxy color-magnitude diagram
- Galaxy Zoo
- William Wilson Morgan
- Fritz Zwicky
References
- ↑ Hubble, E. P. (1936). The Realm of the Nebulae. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 36018182.
- ↑ de Vaucouleurs, G. (1959). "Classification and Morphology of External Galaxies". Handbuch der Physik 53: 275.
- ↑ Binney, J.; Merrifield, M. (1998). Galactic Astronomy. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691025650.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 de Vaucouleurs, G. (1994) (PostScript). Global Physical Parameters of Galaxies. http://www.stsci.edu/institute/conference/galaxy-morphology/devaucouleurs.ps. Retrieved 2008-01-02.
- ↑ Binney, J.; Merrifield, M. (1998). Galactic Astronomy. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691025650.
External links
- Galaxies and the Universe - an introduction to galaxy classification
- Near-Infrared Galaxy Morphology Atlas, T.H. Jarrett
- The Spitzer Infrared Nearby Galaxies Survey (SINGS) Hubble Tuning-Fork, SINGS Spitzer Space Telescope Legacy Science Project
- Go to GalaxyZoo.org to try your hand at classifying galaxies as part of an Oxford University open community project
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||